+918048034088

This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, often abbr...
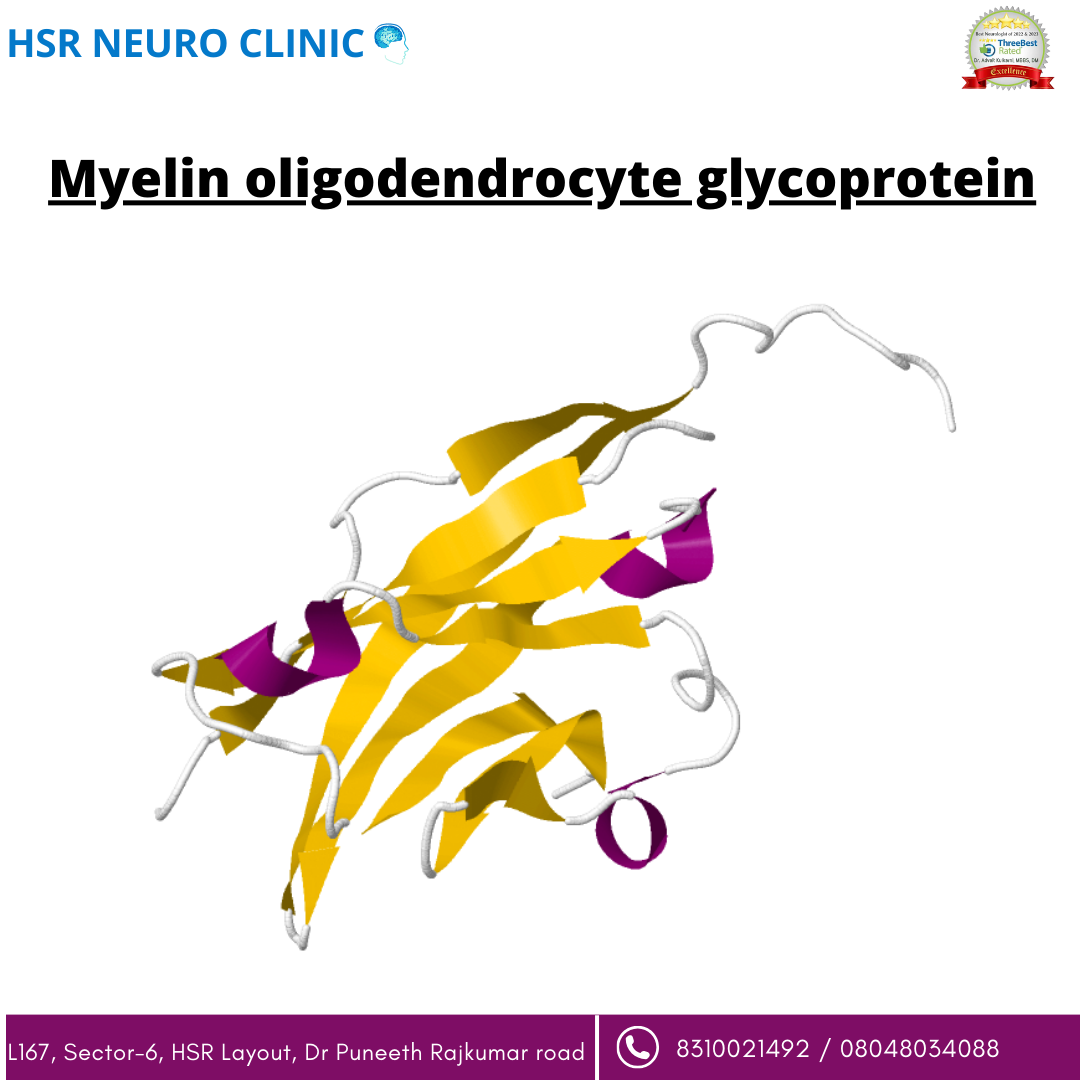
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, often abbreviated as MOG, is a protein found in the central nervous system (CNS) of vertebrates, including humans. It is primarily located on the surface of oligodendrocytes, which are a type of glial cell responsible for producing the myelin sheath that insulates nerve fibers (axons) in the CNS. The myelin sheath acts as an electrical insulator, allowing for efficient transmission of nerve impulses. MOG plays a role in the structure and stability of myelin, and it is also an important antigen. Antigens are substances that can trigger an immune response in the body. In the context of the nervous system, MOG can be a target for the immune system, and in some cases, the immune system may mistakenly attack MOG, leading to demyelination and neurological disorders. Autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), involve the immune system mistakenly attacking components of the CNS, including MOG. When MOG is targeted by the immune system, it can result in demyelination and damage to nerve fibers, leading to the characteristic symptoms of these conditions. Researchers study MOG and its interactions with the immune system to better understand and potentially develop treatments for these diseases.

